The Importance of Cretan Olive Oil
Brief History
The cultivation of olives and the production of olive oil have been intertwined with humanity since time immemorial, according to evidence provided by the objects and archaeological remains of the most ancient civilizations.
The olive tree has been an integral part of life in the eastern Mediterranean since the first appearances of civilization. There are stone mortars and presses used for pressing olive oil and date back to 5000 BC.
Archaeological finds from the Minoan Palaces in Crete are fine examples of the role of olive oil in the Cretan or Minoan civilization, which reached its peak between 2000 and 1450 BC.
From the time of ancient Egypt to modern religions, olive oil has been used in religious ceremonies, and you will find many references to the olive tree in the Old Testament and other sacred texts. After the flood, a dove brought an olive leaf to Noah and told him that the flood waters had receded.
In all civilizations, the olive tree and olive oil occupied central positions in the agricultural economy of the Mediterranean countries and in their trade with neighboring populations. The Minoans of Crete were among the first civilizations to prosper from olive oil, and Crete continues to be a major olive oil producing region to this day.
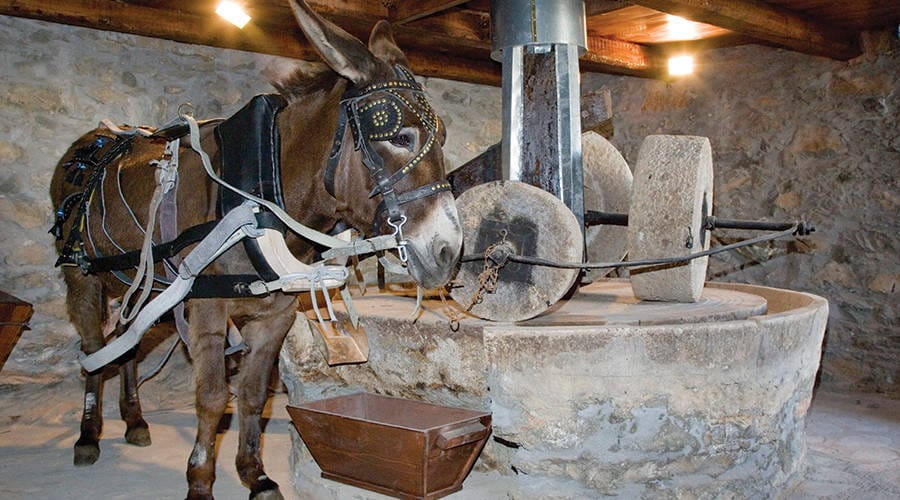
Traditional Olive Oil Production

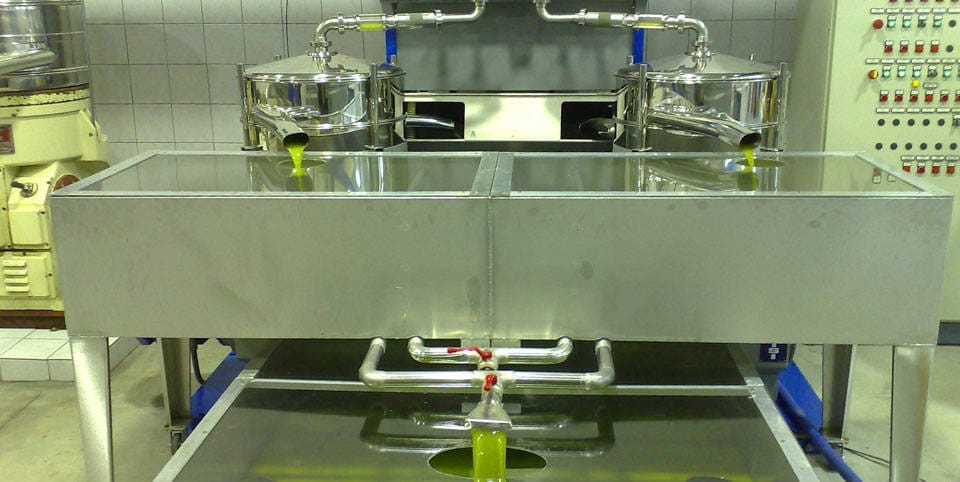
Modern Olive Oil Production

Olive Oil In Ancient Crete
Archaeological findings that prove that the Minoans used olive oil in their daily lives are found everywhere in Crete and especially in the area of Sitia, Lassithi. A particularly impressive discovery is the intact olives with the flesh preserved, which were found at the bottom of a conical cup submerged in a well of water, in one of the four largest Minoan palaces of Crete, the Minoan Palace of Kato Zakros and dated to around 1,600 BC. Findings such as amphorae and large clay pots called Linoi, which were used in the production
of olive oil, have been discovered in many houses surrounding the Palace as well as in Minoan Villas, such as those of Palekastro and Itanos, Sitia.
Many ancient stone olive presses have also been found in Crete. This one at Vathypetro, Archanes is believed to be the oldest in Europe. Olive oil was stored in large pithoi like those found in the West Wing of the Minoan Palace of Knossos, with a total estimated capacity of 250,000 kilograms. The Minoans
used olive oil in their diet, as a cleanser instead of soap, as a base for perfumes and ointments, as medicine, for lighting and for protecting delicate surfaces.
Crete & Peloponnese
Although Cretan olive oil has earned a stellar reputation over the years, it’s important to recognize that both Crete and the Peloponnese produce olive oils of exceptional quality. These two regions of Greece share similar high-quality standards, cultivate the same renowned varieties of olive trees, and enjoy nearly identical climates, making them both ideal for olive cultivation. However, Crete, with its rich history, stunning landscapes,
and thriving tourism industry, has managed to establish a particularly strong brand presence, not only within Greece but also internationally.
The island’s fame has drawn countless visitors who, after experiencing the authentic flavors firsthand, bring home the reputation of Cretan olive oil. This combination of tradition, culture, and tourism has solidified Crete’s position as a global ambassador for Greek olive oil.
Cretan – Greek Olive Oil Importance
In Greece today, olive oil is almost sacred. The Greek people are the largestper capita consumers of olive oil in the world: the national average consumption ranges from 18 liters to over 30 liters per person. The highest consumption certainly belongs to the Cretans where the annual consumption per person was on average 31 liters, according to a 1996 study. The basic ingredient for sauces in Greek cuisine is olive oil, which can be soy sauce
for the Chinese or Worcestershire sauce for the English. Greek olive oil is more than just a sauce, of course, but it is the prerequisite without which Greek cuisine as we know it would not exist. In the English-speaking world, a recipe for a Greek dish usually calls for two tablespoons of oil. The same recipe in a Greek household calls for half a cup. Anywhere in Crete it calls
for a full cup.
An authentic Greek or Cretan dish, to a traveler, seems abundant in olive oil.
You might say that so much oil has too many calories and too much fat. But, it is really the fuel for the Greeks, and Greek olive oil, especially the Cretan variety, is a very healthy food and the most powerful fuel.
Many studies have shown that a Mediterranean diet low in saturated fats but rich in monounsaturated fats such as olive oil, whole grains, fruits and vegetables, helps prevent heart disease and even cancer. Another study reported a few years ago in the New England Journal of Medicine found that following a Mediterranean diet in a Greek population significantly reduced mortality risks, especially the risks of death from heart disease and cancer. The traditional diet evaluated included plenty of olive oil, plenty of vegetables and fruits, nuts, cereals and moderate intake of fish and wine. All diets believed to provide these benefits are high in monounsaturated fats, mainly from olive oil, which plays the most important role in this protective effect.
It should be remembered that the ideal climates of Greece and Crete contribute favorably to the superiority of olive oil. It has a richer, fruity flavor, intense aroma and a distinctive green color. The intense sunshine of Greece and its islands generously produces anthocyanins, flavonoids and phenols. The benefits of Greek olive oil have been sufficiently proven. The best way
to get to know it better is to incorporate olive oil into your diet.
Different Types of Olive Varieties for Cretan – Greek Olive Oil
Koroneiki
The “queen” of olives, produces a high-quality, low-acid, full-bodied extra virgin olive oil. The Koroneiki olive variety, picked when still green, has been awarded many times for its strong aromatic oil, ideal to enjoy raw, in its natural state or to add at the end of cooking. This type of olive yields approximately 6 to 7 liters of the best olive oil that has a golden-green color and is extremely famous for its fruity and fresh flavor. The Koroneiki olive is mainly found in the southern Peloponnese and in some areas of Crete.
The Kalamata PDO is one of the best extra virgin olive oils derived from the Koroneiki variety.
Athinolia
Athinolia is a late-ripening olive variety that is harvested from late
December to early January. Its fruit is oval in shape and medium in size, weighing from 2.2 to 2.9 grams and a length that can range from 7.5 to 25 millimeters. When the Athinolia and Koroneiki olive varieties are mixed, they produce an extra virgin olive oil with a full body and a balanced and distinctive fruity flavor.
Manaki
Manaki is another olive variety that ripens slowly. This olive variety thrives at very high altitudes. The harvest season is from late October to early January. The fruit is oval in shape and is relatively small. The flavor of the olive oil produced from this fruit is softer and its aroma is reminiscent of ripe fruits such as apple and tomatoes.
Different Types of Olive Oils for Cretan – Greek Olive Oil
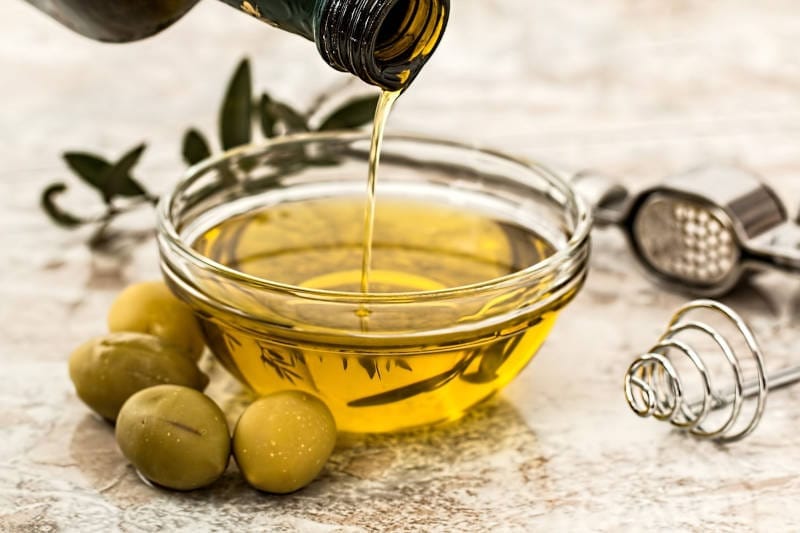

Extra Virgin Olive Oil
This is the best quality olive oil with an acidity that does not exceed 0.8% per 100 grams. Its taste and aroma are reminiscent of the taste of freshly picked olives, however, depending on the variety we choose, we will have a different taste result. For this reason, it may be useful to have two or three different varieties in our cupboard. It is extremely valuable for our health and our first choice in cooking.
Virgin Olive Oil
It has a mild aroma, pleasant taste and acidity that does not exceed 2.0% per 100 grams.
Olive Oil
This is a blend of refined and virgin olive oils with an acidity of less than 1.0% per 100 grams. It has a lower nutritional value than virgin olive oil.
Lampante Olive Oil
It has an acidity of more than 2.0% per 100 grams and is not suitable for consumption. It is mainly intended for refining or refinement as it is also called for industrial use.
Refined Olive Oil
It is obtained from the refinement of virgin olive oils, while its acidity does not exceed 0.3% per 100 grams. It is inferior in terms of vitamins and nutrients and is not particularly bitter, due to its lack of antioxidants.
Pomace Oil
It is the result of mixing refined pomace oil and virgin olive oils, except for lampante olive oil. Its acidity does not exceed 1.0% per 100 grams.
Crude Pomace Oil
It says it all in its name. It is obtained from olive kernels, after treatment with solvents or natural means or it is the oil that corresponds, with the exception of certain special characteristics, to Lampante olive oil.
Refined Pomace Oil
It is obtained from the refinement of crude pomace oil and the acidity does not exceed 0.3% per 100 grams.
Conclusion
At Roots And Crops, we believe in the authenticity and quality of every olive oil brand, and we do not favor one over the other. In our store, we proudly offer a single, hand-selected brand of olive oil that reflects our commitment to sustainability and excellence. This olive oil is 100% organic, sourced from carefully chosen fields that we know intimately and trust. It is the very same oil produced by our family, with every step of the process being closely monitored and crafted to perfection. From the harvest to the bottle, we can confidently say that this olive oil is the result of decades of experience and dedication, resulting in a rich, full-bodied flavor that stands out with every drop. We take pride in offering our customers a product that is not only delicious but also an authentic reflection of our family’s values and passion for quality.